Certified Medication Aide (MACE) Practice Tests & Test Prep by Exam Edge - Free Test
Our free Certified Medication Aide//Assistant (MACE) Practice Test was created by experienced educators who designed them to align with the official National Council of State Boards of Nursing content guidelines. They were built to accurately mirror the real exam's structure, coverage of topics, difficulty, and types of questions.
Upon completing your free practice test, it will be instantly reviewed to give you an idea of your score and potential performance on the actual test. Carefully study your feedback to each question to assess whether your responses were correct or incorrect. This is an effective way to highlight your strengths and weaknesses across different content areas, guiding you on where to concentrate your study efforts for improvement on future tests. Our detailed explanations will provide the information you need to enhance your understanding of the exam content and help you build your knowledge base leading you to better test results.
Login or Create an Account to take a free testAfter you have completed your free test you will receive a special promo code that will save your between 10-15% on any additional practice tests!
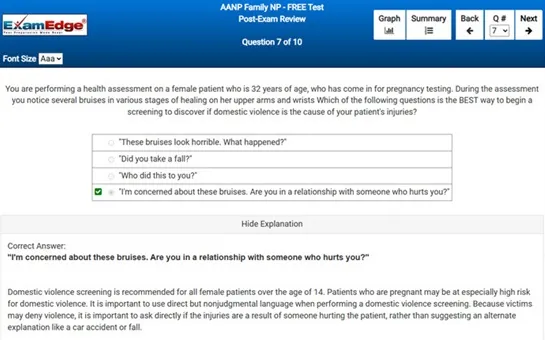
** Sample images, content may not apply to your exam **