MCA Elem Ed MC All Subtests (07-010) Practice Tests & Test Prep by Exam Edge - Topics
** Sample images, content may not apply to your exam **
Understanding what is on the MCA Elem Ed MC All Subtests exam is crucial step in preparing for the exam. You will need to have an understanding of the testing domain (topics covered) to be sure you are studying the correct information.
- Directs your study efforts toward the most relevant areas.
- Ensures efficient and adequate preparation.
- Helps identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Allows for a focused approach to address gaps in understanding.
- Aligns your preparation with the exam's expectations.
- Increases the likelihood of success.
- Keeps you informed about your field's current demands and standards.
Not ready to purchase our complete practice tests yet? Start with a MCA Elementary Education Multi-Content All Subtests FREE Practice Test first!
Understanding the exact breakdown of the MCA Elementary Education Multi-Content All Subtests test will help you know what to expect and how to most effectively prepare. The MCA Elementary Education Multi-Content All Subtests has 160 multiple-choice questions The exam will be broken down into the sections below:
| MCA Elementary Education Multi-Content All Subtests Exam Blueprint | ||
|---|---|---|
| Domain Name | % | Number of Questions |
| English Language Arts | ||
| Foundations of Language and Literacy Development | 25% | 10 |
| Text Comprehension and Vocabulary Development | 25% | 10 |
| Reading Literature and Informational Texts | 25% | 10 |
| Processes, Modes, and Conventions of Written and Oral Communication | 25% | 10 |
| Mathematics | ||
| Numbers and Operations | 40% | 16 |
| Algebraic Relationships | 35% | 14 |
| Measurement, Geometry, and Data | 25% | 10 |
| Science | ||
| Science and Engineering Practices and Crosscutting Concepts | 35% | 14 |
| Biology | 30% | 12 |
| Physical Science and Earth Science | 35% | 14 |
| Social Studies | ||
| History | 34% | 14 |
| Geography | 33% | 13 |
| Government and Economics | 33% | 13 |
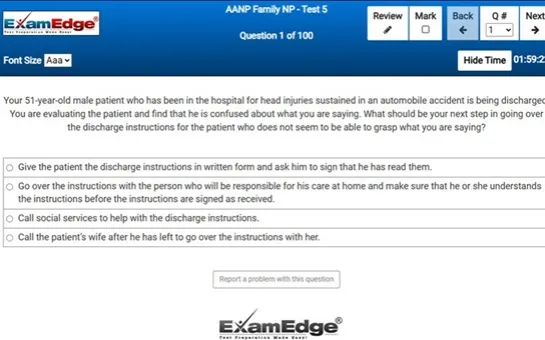
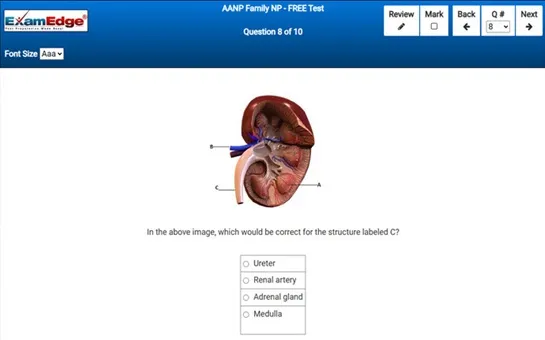
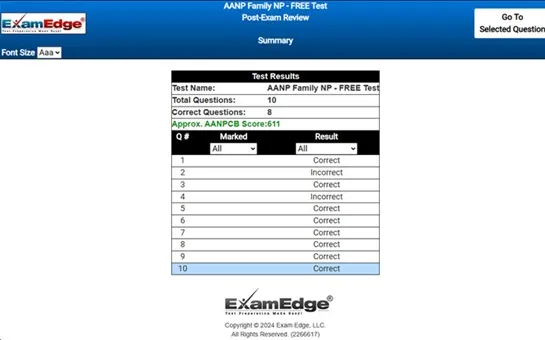
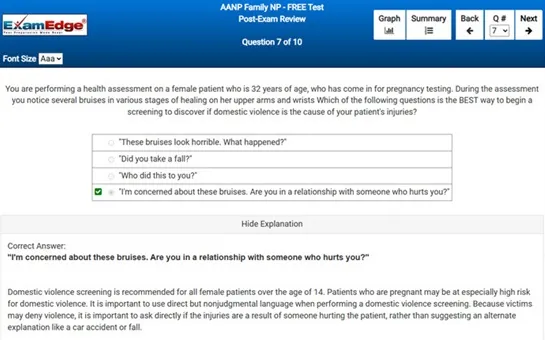
MCA Elementary Education Multi-Content All Subtests - Exam Topics Sample Questions
|
|